1. What is Reported Speech?
Reported speech is the form of speech used to express what was said by a person at some point in time. This article will help you understand what reported speech is, when to use it, and provide examples to make learning easy.
Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “Reported speech is speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.”
Cambridge Dictionary defines it as “Reported speech is how we represent the speech of other people or what we ourselves say.”

Change of Pronoun in Reported Speech
| I | He, she |
| Me | Him, her |
| We | They |
| Us | Them |
| You | He she they |
| You | Him her them |
| My | His her |
| Mine | His hers |
| Our | Their |
| Ours | Theirs |
| Your | His her their |
| Yours | His hers theirs |
Change of Adverbs of Place and adverbs of time
| Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
| This | That |
| These | Those |
Adverbs of Place
| Here | There |
Adverbs of Time
| Now | Then |
| Today | That day |
| Tomorrow | The next day |
| Yesterday | The previous day |
| Last week | The week before |
| Next week | The week after |
| Ago | Before |
| Thus | So |
| Last month | The previous month |
| Next month | The following month |
| Hence | Thence |
| Day before yesterday | Day before the previous day |
| Day after tomorrow | Day after the next day |
| Tonight | That night |
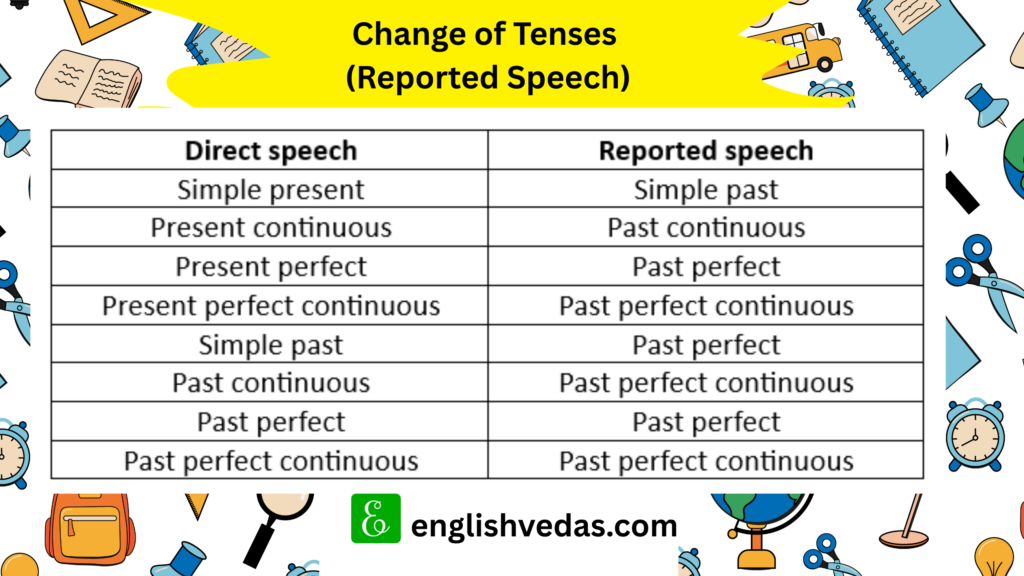
Change of Tenses
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
| Simple present | Simple past |
| Present continuous | Past continuous |
| Present perfect | Past perfect |
| Present perfect continuous | Past perfect continuous |
| Simple past | Past perfect |
| Past continuous | Past perfect continuous |
| Past perfect | Past perfect |
| Past perfect continuous | Past perfect continuous |
Change of Modal Verbs
| Direct speech | Reported speech |
| Will | Would |
| May | Might |
| Can | Could |
| Shall | Should |
| Has /Have | Had |
Change of Pronouns (Reported Speech)
- First person pronouns are changed into pronouns of the same person as the person of the subject of the reporting verb.
Direct: I said, “I have done my homework.”
Indirect: I said that I had done my homework.
Direct: You said, “I have done my homework.”
Indirect: You said that you had done your homework.”
Direct: She said, “I have done my homework.”
Indirect: She said that she had done her homework.
- Pronouns of the second person are changed into pronouns of the same person as that of the object of the reporting verb.
Direct: Ravi said to me, “You should do your homework every day.”
Indirect: Ravi told me that I should do my homework every day.
Direct: Ravi said to him, “You should do your homework every day.’
Indirect: Ravi told him that he should do his homework every day.
Change of Verbs denoting time and position
All pronouns, adjectives or adverbs denoting nearness of time or position must be replaced by words denoting corresponding remoteness or distance.
Direct: He said, “I am glad to be here this afternoon.”
Indirect: He said that he was glad to be there that afternoon.
Direct: I said, “These apples are fresh.”
Indirect: I said that those apples were fresh.
Direct: He said, “I have got a guitar lesson today.”
Indirect: He said that he had got a guitar lesson that day.
Direct: She said, “I will start my English lessons next month.”
Indirect: She said that she would start her English lessons the following month.
Direct: He said, “He visited Australia last year.”
Indirect: He said that he had visited Australia the previous year.
Change of Tenses
- In reported speech the simple present gets converted to simple past.
Example: John said, “I play cricket.”
John said that he played cricket.
- Present continuous tense in direct speech gets converted to past continuous tense.
Example: Mohan said, “I am dancing in my room.”
Mohan said that he was dancing in his room.
- Present perfect gets converted to past perfect in reported speech.
Example: Sue said, “I have read the newspaper.”
Sue said that she had read the newspaper.
- Present perfect continuous changes into past perfect continuous in reported speech.
Example: Sita said, “I have been cleaning my room.”
Sita said that she had been cleaning her room.
- Simple past in indirect speech gets converted to past perfect in reported speech.
Example: Diane said, “I played the piano.”
Diane said that she had played the piano.
- Past continuous changes to past perfect continuous in reported speech.
Example: Sam said, “I was running in the park.”
Sam said that he had been running in the park.
- Past perfect in direct speech remains as past perfect in reported speech.
Example: Tina said, “I had bought a car.”
Tina said that she had bought a car.
- Past perfect continuous remains unchanged in reported speech.
Example: Fiona said, “I had been listening to music.”
Fiona said that she had been listening to music.
Change of Modal Verbs (Reported Speech)
- In reported speech, ‘will’ changes to ‘would’.
Example: Tom said, “I will phone you.”
Tom said that he would phone me.
- Can changes to could in reported speech.
Example: Peter said, “I can’t find my keys.”
Peter said that he couldn’t find his keys.
- ‘Have’ or ‘has’ changes to ‘had’.
Example: Sarah said, “I have to wait for my friend.”
Sarah said that she had to wait for her friend.
- ‘Shall’ changes to ‘should’ in reported speech.
Example: Mohan said, “Shall I go for a walk.”
Mohan asked if he should go for a walk.
- ‘May’ changes to ‘might’ in reported speech.
Example: He said, “I may go to New York next week.”
He said that he might go to New York the following week.
Examples of reported Speech
- Sarah said that she was enjoying her new job.
- He said that he was very busy.
- She said that she needed it.
- Neha assured that she would reach home by 7 pm.
- Mike said that he had gone to the dentist the previous day.
- Olive asked Betty if she would accompany her to the party.
- Ann and Martin said that they were going to buy a house.
- Alice said that she had to go early.
- Priya asked me if I knew where her notebook was.
- Steve said that he wanted to watch TV.
- He said that he would leave those papers there.
- I told my colleague that I would attend the office the following week.
- Jack told his teacher that he had forgot to bring his notebook that day.
- The hawker said that he would sell all those articles there.
- You told me that you had met my brother two years before.
- She told me that I was always welcome to her house.
- The astrologer told her that her chances of success were bright.
- Mr. Kapoor said that this morning he is going to buy a new car soon.
- My teacher said that Gandhiji died in 1948.
- He told his son that the Taj mahal was built by emperor Shahjahan.
Reported Speech Exercise 1
Convert the following sentences into indirect speech.
- Priya said, “Ravi has gone home.”
- Brian said, “I am not hungry.”
- You have told me, “She is a good dancer.”
- The traveller said, “Here I slept for two hours.”
- The hermit said to the king, “Man is immortal.”
- Linda said, “I am going to the cinema.”
- John and Sharon said, “We haven’t got a key.”
- Neha said, “I have just come back from holiday.”
- Sue said, “I can’t go to the market.”
- My teacher said to me, “Light travels in a straight line.”
Reported Speech Exercise 2
Convert the following sentences into direct speech:-
- He said he studied English every evening.
- The teacher said that the Earth goes around the sun.
- John said that he had been cheated.
- Diane told Sue that she likes her bag.
- He told Jack that he was an intelligent boy.
- Peter ordered his servant to do that work.
- The mother asked her son to do his homework.
- I asked my aunt if she could take dinner with me.
- The gardener stopped the boys from plucking flowers in the garden.
- The football team shouted with joy that they had won the match.
People Also ask:-
1. What is reported speech?
Reported Speech is repeating someone’s words and expressing it indirectly as one’s own words. We don’t use quotation marks in it, and change the tense also.
2. Do we always change the tense in reported speech?
Yes, we change the tense of the verb into past tense.
For instance:
Direct: He said, “I am thirsty.”
He said that he was thirsty.
Reported Speech Worksheet
Reported-speech-worksheetAlso Read:-
- Must and Have to: Surprising Difference Clarity and Exercise
- Mastering Each and Every Difference Use 30 Example Sentences: Best
- Mastering the Past Perfect Continuous Tense: 30 Example Sentences and Exercises to Boost Your Grammar Skills
- 100 Powerful Examples of Future Continuous Tense and Structure
- At On In: Difference Worksheet Exercises That Make Learning Easy and Simple!
- 5 Simple Ways to Learn Spelling
- Informative Debate |The Internet Curbs Creativity: 5 Points for and Against
- Why India Celebrates National Space Day on August 23?
- Understanding Infinitives: Uses of To and Without To | Simple Examples | 1 Exercise
- Complex Sentence Examples for Easy Grammar Learning

Written by Sukhjit Kaur, English educator with 17+ years of experience helping students master grammar and writing. Through EnglishVedas.com, she simplifies English grammar using examples from daily life and classrooms.

